Antifungal resistance, though less discussed than antimicrobial resistance, is emerging as a significant global health concern. Experts warn that fungal infections, or mycoses, are becoming more difficult to treat due to increasing resistance to antifungal drugs. While these infections might not mirror the apocalyptic fungal outbreaks seen in popular media like The Last of Us, they are quietly spreading, especially in hospital settings, leaving individuals, particularly those with weakened immune systems, vulnerable to potentially fatal diseases.
According to the French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS), the overuse and misuse of antifungal treatments are driving the rise in antifungal resistance. This trend mirrors the situation with antimicrobial resistance, where bacteria become resistant to antibiotics due to excessive use, not only in medical settings but also in agriculture, where antibiotics are used in animal feed. The CNRS highlights that antifungal agents, much like antibiotics, are extensively used in agriculture and in human and animal health, leading to similar mechanisms of resistance across both types of treatments.
The World Health Organization (WHO) took a significant step in recognizing the gravity of this issue when it compiled a list of “19 particularly dangerous fungi” in 2022. The WHO has noted that the incidence and geographical spread of fungal diseases are expanding worldwide, with antifungal resistance being a major driver of this growth. These infections are especially dangerous for people with compromised immune systems, as they can cause severe health complications.
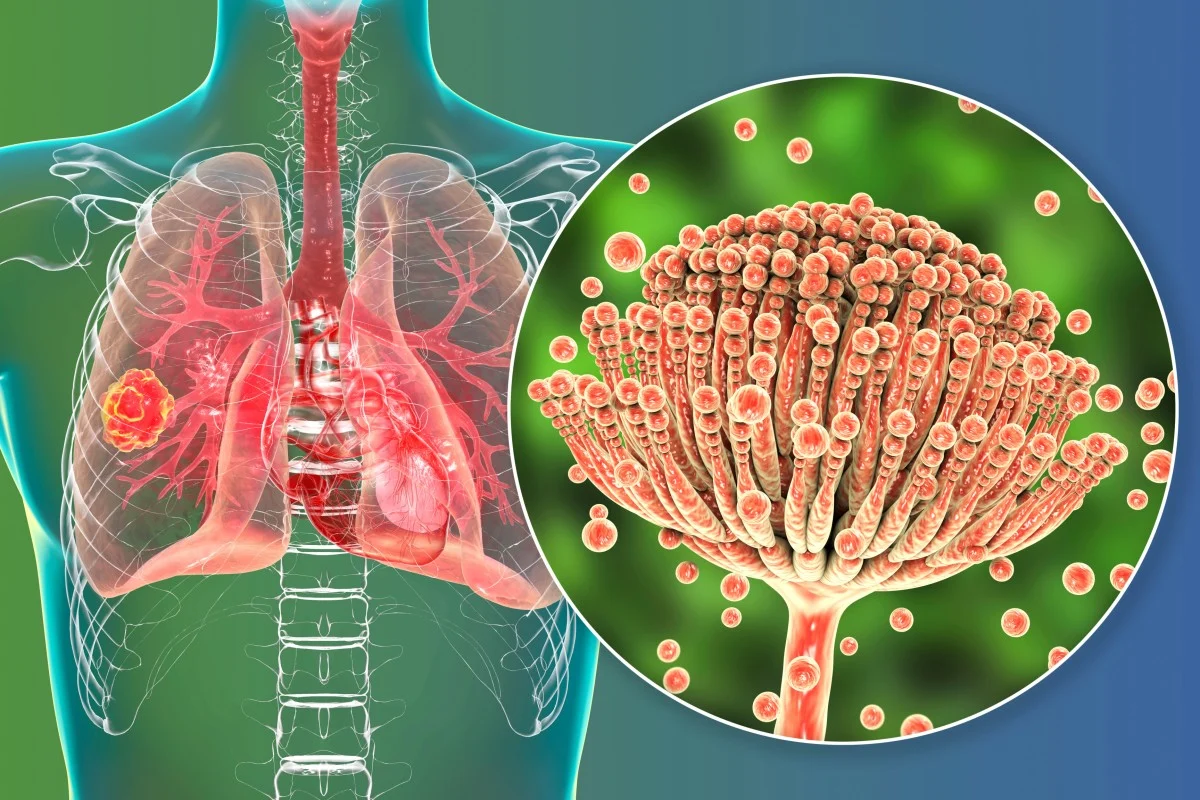
One example of a dangerous fungus is Aspergillus fumigatus, a common mold found in soil that can cause lung disease in vulnerable individuals. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has reported that antimicrobial resistance is emerging in Aspergillus, making it more difficult to treat. Other notable fungal diseases include blastomycosis, which also affects the lungs, and Candida auris infection, caused by Candida auris, a yeast that can lead to severe illness and spreads easily in healthcare facilities.
The increasing resistance to antifungal drugs, compounded by their overuse, poses a growing health risk. Without effective treatments, patients may face longer recovery times and higher mortality rates, making antifungal resistance a hidden but critical global health crisis.
READ MORE: